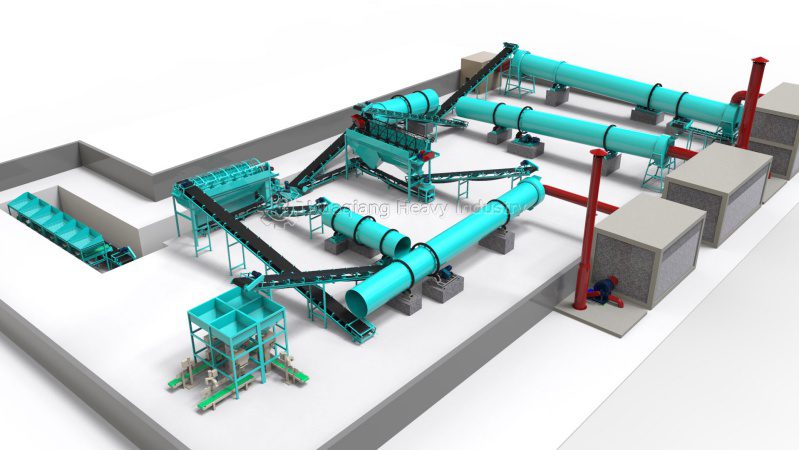
The integration of NPK fertilizer production lines and granulation equipment is central to advancements in modern agricultural technology, driving precision agriculture towards efficiency and sustainability. NPK fertilizers contain nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), essential nutrients for crop growth. In precision agriculture, these fertilizers are applied in a data-driven manner, enabling targeted nutrient supply. Key features of the production line include raw material adaptability and flexible formulation, handling materials such as urea, ammonium phosphate, and potassium chloride. Automated systems adjust the N:P:K ratio, supporting variable rate fertilization (VRFA). For example, prescription maps generated from soil tests allow for precise application of NPK in different areas of the field, avoiding waste.
Granulation equipment is a critical component of the NPK fertilizer production line, with common methods including extrusion granulation, tower granulation, and agglomeration. Extrusion granulation requires no additional drying and produces high-strength granules, suitable for low-concentration compound fertilizers; tower granulation optimizes slurry flowability, ensuring uniform granules; and agglomeration offers low investment and rapid deployment, producing granules with good storage properties. These devices improve the physical properties of fertilizers, such as solubility and slow-release characteristics. Combined with sensor technology in precision agriculture, ion-selective electrodes and spectroscopy are used to monitor soil N, P, and K levels in real-time. Innovations in nano-NPK fertilizer granulation provide a slow-release mechanism, reducing conventional fertilizer use by 25%-50%, and significantly increasing yields in crops like corn and potatoes.
The production line integrates automated control, such as PLC and AI monitoring, enabling continuous production and high-capacity adjustments. The drying and cooling process utilizes drum dryers, supporting energy recovery and reducing power consumption, adhering to the 4Rs principle (right source, rate, time, and place). In precision agriculture, water-soluble NPK is precisely delivered through drip irrigation systems, combined with satellite imagery and GPS to optimize fertilization timing, reducing leaching losses and greenhouse gas emissions.
In practical applications, high-capacity production lines and granulation equipment in European factories have increased crop yields by 20%-30% and reduced costs by 30%. Developing countries like India are using these technologies to adapt to climate change, supporting smallholder farmers with mobile apps for customized fertilizer recommendations. Challenges include high initial investment, but the proliferation of IoT and AI is addressing this issue. In the future, production lines and granulation equipment will integrate quantum computing to enable global soil data feedback. In summary, the integration of NPK fertilizer production lines and granulation equipment not only optimizes the production process but also directly serves precision agriculture, enhancing food security and environmental sustainability. Through continuous innovation, this system will become a cornerstone of Agriculture 4.0.